Portable Generator Buying Guide
Types of Portable Power Units
- Conventional/Traditional Generators: Powerful and suitable for heavy tools or home backup. However, they’re often louder and produce less stable power, which may not be ideal for sensitive electronics. Typically fueled by gasoline or diesel.
- Inverter Generators: Quieter and more fuel-efficient than traditional types. They produce clean, stable electricity, making them safe for laptops, phones, and other sensitive devices. Learn more about top inverter generator picks.
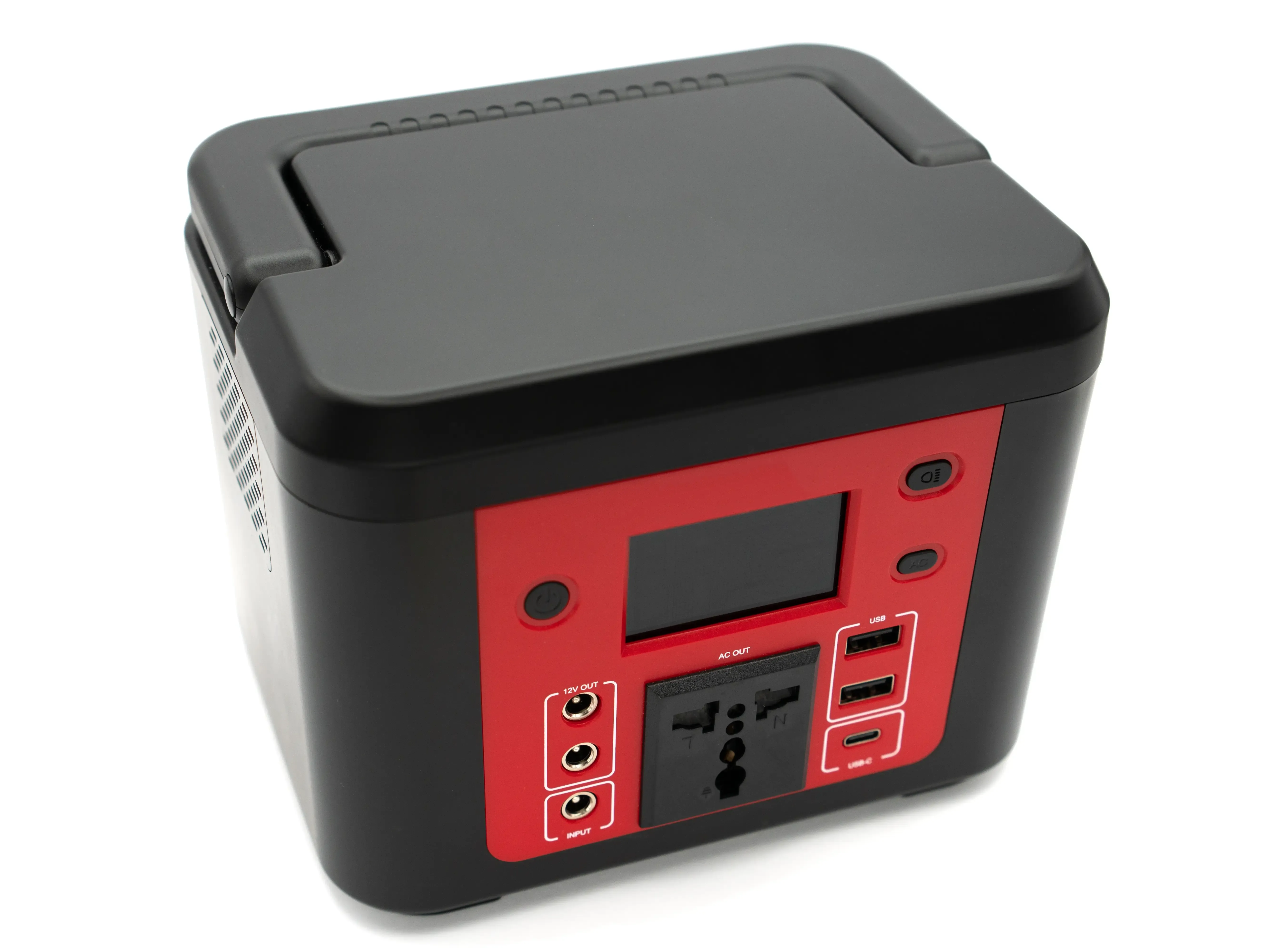
- Portable Power Stations (Battery Generators): Silent and emission-free, these use stored battery power recharged via AC, DC, or solar. Perfect for indoor use, off-grid applications, or sensitive electronics. Learn about choosing the right battery capacity.
Output Power (Running Watts & Surge Watts)
Running wattage is the continuous power output, while surge wattage is the short burst of power available during startup. Ensure your generator meets both the continuous and peak demands of your devices.
Fuel Type
Generators can run on various fuel types. Gasoline is common for short-term use. Propane burns cleaner and stores longer. Battery-based stations use stored energy and are ideal for indoor or emission-sensitive scenarios. Consider fuel availability, storage needs, and eco-friendliness when deciding.
Portability
The portability of a unit is largely determined by its weight and form factor.
| Type of Unit | Estimated Weight | Capacity Range | Common Use Cases | Transportability |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Smaller, Lighter | Under 15 lbs | 300–500Wh | Backpacking, camping, small device charging | Very portable; one-hand carry |
| Mid-Range | 15–50 lbs | 500Wh–1500Wh | RVing, car camping, short home backup | Portable with handles; two-hand lift for some units |
| Larger, Heavier | 50 lbs and above | 2000Wh and up | Whole-home backup, off-grid setups, long emergencies | Usually includes wheels or trolley handles |
Starting Mechanism
Generators may feature:
- Recoil Start: Pull cord mechanism (standard on many gas generators)
- Electric Start: Push-button ignition
- Remote Start: Activation via key fob or mobile app
Battery-powered stations typically use a button or app. Electric and remote starts add convenience, especially in emergencies or for elderly users.

Why You Should Trust Us
Our buying guides are crafted with precision and objectivity. We rely exclusively on manufacturer data, third-party testing, and established standards to deliver unbiased, fact-based insights.
Each product recommendation undergoes thorough evaluation, ensuring our guidance remains free from promotional influence and focused on your best interest.
Final Thoughts
From quiet, clean inverter models to heavy-duty fuel-powered units, the portable power landscape is full of strong options. For those seeking the ultimate in expandable backup power, the EcoFlow DELTA Pro 3 stands out with immense capacity and rapid recharge. Meanwhile, the Champion 4750-Watt Dual Fuel Generator remains a top pick for value, reliability, and fuel flexibility.
Ultimately, your ideal generator depends on your needs, space, and budget. Use this guide to confidently choose a power solution tailored to your lifestyle.
FAQs
1. How can I tell if my generator is overloaded?
Signs of generator overload include straining engine sounds, dimming lights, or tripped breakers. Many newer models feature warning displays or error codes to alert you of excessive power draw.
2. How big of a generator do I need for my house?
For essential appliances (fridge, lights, medical devices), a 3,000–5,000W unit may be sufficient. Whole-home coverage may require 7,500W or more and possibly a transfer switch for safety.
3. Can a portable generator run my air conditioner?
Yes, but it depends on the AC unit size. A small window AC might need 3,000–4,000 running watts. Central AC units often need much more, and a soft start kit may help reduce starting surge requirements.